How to Read a VFD Nameplate – Full Guide for Installers and Engineers
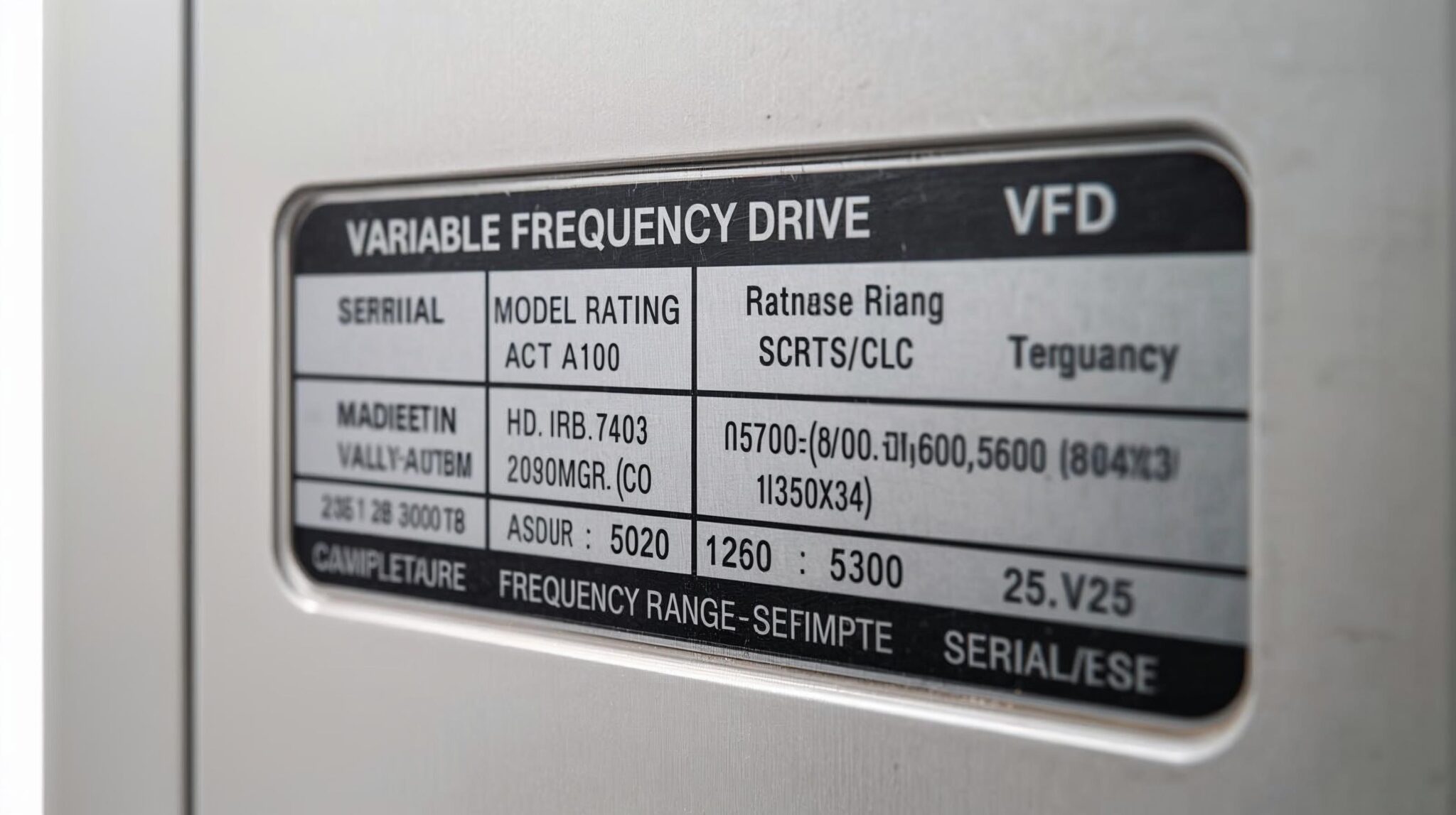
Every Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) comes with a factory label — but many installers overlook how much critical information it contains. The nameplate tells you everything from voltage and current ratings to firmware version and environmental tolerances.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to read a VFD nameplate correctly, what each field means, and how to match it to your application.
📄 What Is a VFD Nameplate?
A VFD nameplate is a permanent label affixed to the drive housing that provides key electrical, mechanical, and identification data. It’s essential for:
- ✅ Verifying correct installation
- ✅ Sizing and wiring the motor/load
- ✅ Programming the drive parameters
- ✅ Troubleshooting and part replacement
Different brands use different formats, but most include the same core fields.
🔍 Common VFD Nameplate Fields Explained
Here’s a breakdown of what you’ll typically find on a VFD nameplate:
- Model Number: The exact series/type of drive (e.g. ACS355-03E-07A3-4)
- Input Voltage: Acceptable input range (e.g. 3-phase 380–480V AC)
- Input Frequency: Usually 50/60 Hz
- Output Voltage: Max drive output to motor, usually = input
- Output Current: Max continuous current to motor (e.g. 11 A)
- Output Frequency: Adjustable range, e.g. 0–400 Hz
- Power Rating: In kW or HP (e.g. 4.0 kW)
- Enclosure Rating: IP20, IP55, or IP66
- Serial Number: Used for warranty & tech support
- Firmware Version: Important for compatibility and updates
🛠️ Example – ABB ACS355 Nameplate
Here’s a real-world example from an ABB ACS355 unit:
- Model: ACS355-03E-07A3-4
- Input: 3PH 380–480V, 50/60Hz
- Output: 3PH 0–480V, 0–500Hz, 7.3 A
- Power: 4.0 kW
- Protection: IP20
- Firmware: v1.14
This tells you the unit is rated for 3-phase 400V systems and can control up to a 4 kW motor at full load. It also shows the rated output current (7.3 A), important for motor selection and overload protection.
⚠️ Why It Matters
Misreading or ignoring a VFD nameplate can lead to:
- ❌ Oversized/undersized motors
- ❌ Faults from voltage mismatch
- ❌ Overheating from overloads
- ❌ Missed firmware incompatibilities
📌 Always match your drive and motor specs — especially when replacing units.
🧪 Pro Tip: Use the Model Code to Unlock Full Specs
Most VFD part numbers encode the following:
- 🔢 Series type (ACS355, ACS880, MS300, etc.)
- 📏 Voltage class (e.g. 01E = 1-phase, 03E = 3-phase)
- 📉 Output current rating (e.g. 07A3 = 7.3 A)
- 🔄 Frequency & enclosure class
🛒 Shop by part number at Drive Outlet Megastore for full traceability and support.
📞 Need Help Reading a Nameplate?
If you’re unsure what your VFD label means, contact our team or use our VFD Sizing Calculator.
Explore VFDs by brand: